Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, is a common disease that makes it difficult for individuals to live comfortably. In this guide, one of the top gastro specialist in Dwarka, Delhi, Dr Rohit Goyal shares the details about piles, covering everything from causes and symptoms to diagnosis, treatment in Delhi, and essential changes, including dietary considerations Lets start with understanding piles
What are Piles or Hemorrhoids?
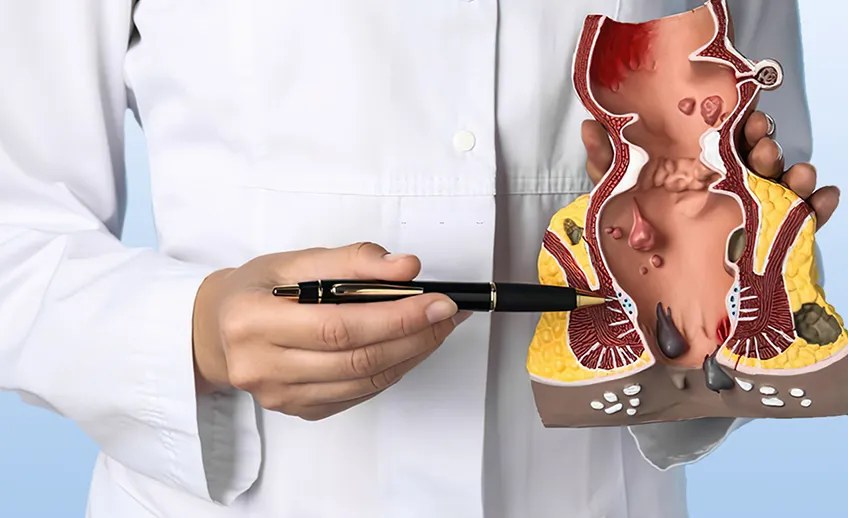
Piles are swollen and inflamed blood vessels in the rectum and anus that cause a lot of discomfort, bleeding, and itching. The exact cause isn’t always clear, but factors like straining during bowel movements, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle are responsible for causing it.
Symptoms of Piles
Persistent itching, discomfort, and pain during bowel movements are common complaints. Rectal bleeding, especially after passing stool, is a telltale sign. Piles can also cause lumps near the anus, making sitting uncomfortable.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the symptoms of piles:
- Bleeding: Blood is noticed on toilet paper after wiping, in the toilet bowl, or on the surface of stools. The blood is bright red, indicating it comes from the lower part of the bowels.
- Pain and Discomfort: Pain or discomfort is felt around the anus during and after bowel movements. The pain vary from mild to severe, and it is throbbing, aching, or sharp.
- Itching and Irritation: Piles cause intense itching in and around the anus. Irritation is a result of mucous leakage from the piles, that irritate the skin.
- Swelling or Lump Near the Anus: In some cases, individuals feel a lump or swelling near the anal opening. This can be internal or external, depending on the location of the piles.
- Incomplete Bowel Movements: Piles create a sensation of incomplete bowel movements even after passing stools.
- Protrusion During Bowel Movements: Piles stick outside the anal opening during bowel movements and retract afterwards. This is known as a prolapsed haemorrhoid.
- Mucous Discharge: Piles lead to the production of excess mucous, which is noticed during or after bowel movements.
Diagnosis
Gastroenterologists perform a physical examination, including a rectal exam, to assess the extent and severity of the piles. In some cases, tests like a sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy are recommended.
Piles Treatment in Delhi
Dr Rohit Goyal explains the following Piles treatment options in Delhi:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Increase fibre intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Fiber softens stools, making them easier to pass, and reducing strain. Drink plenty of water to maintain hydration and soften stools. Engage in regular physical activity to promote bowel regularity and prevent constipation.
- Medicines: Local creams provide relief from itching and inflammation. A Gastro specialist usually prescribes topical medications.
- Sitz Baths: Soaking the affected area in warm water, known as sitz baths, alleviates discomfort and promote healing. Sitz baths are done several times a day for around 10-15 minutes.
- Rubber Band Ligation: A Small rubber band around the base of a hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid shrinks and falls off.
- Injection (Sclerotherapy): A chemical solution is injected into the blood vessel feeding the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink. This is used for smaller hemorrhoids.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical treatment for severe cases or when other treatments have failed. Hemorrhoidectomy is cutting out the hemorrhoidal tissue.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy (PPH): This surgical procedure involves stapling the hemorrhoids to reduce blood supply, causing them to shrink.
When Piles Surgery is recommended?
Doctors recommend piles surgery in cases when conservative treatments, lifestyle modifications, and medications fail to provide relief from persistent and severe symptoms. Surgery is often considered for larger hemorrhoids that cause discomfort. When hemorrhoids develop blood clots (thrombosis), causing severe pain and swelling.
Risks related with piles surgery
The following risks are related to surgery:
- Postoperative pain is common with traditional hemorrhoidectomy.
- Bleeding is normal after surgery but should be monitored.
- Infection at the surgical site is a potential risk.
- Difficulty in urination may occur temporarily.
- Rarely, patients may experience difficulty controlling bowel movements.
Dietary Considerations
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Incorporating fibre-rich foods into your diet can soften stools and make them easier to pass, reducing the strain on hemorrhoids. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources of fibre.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water to maintain soft and bulky stools, easing the passage during bowel movements.
- Limiting Processed Foods: Processed foods, especially those low in fibre, can contribute to constipation and aggravate piles. Cut down on processed snacks and opt for whole, unprocessed foods.
- Adequate Fluid Intake: Besides water, including fluids like herbal teas and natural fruit juices in moderation can contribute to overall hydration.
- Avoiding Spicy Foods: Spicy foods can irritate the digestive system and exacerbate symptoms. Limiting their consumption can help manage discomfort.
- Regular Meals: Establishing a regular eating routine can regulate bowel movements, preventing the strain that contributes to piles.
Piles also called hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed blood vessels in the rectum and anus that makes it difficult for people to live comfortably. Top Gastroenterologist in Dwarka, Delhi has explained the treatment options for the patients along with the diet requirements for the disease. One can consult the doctor before going for surgery or medicines to ensure proper treatment.